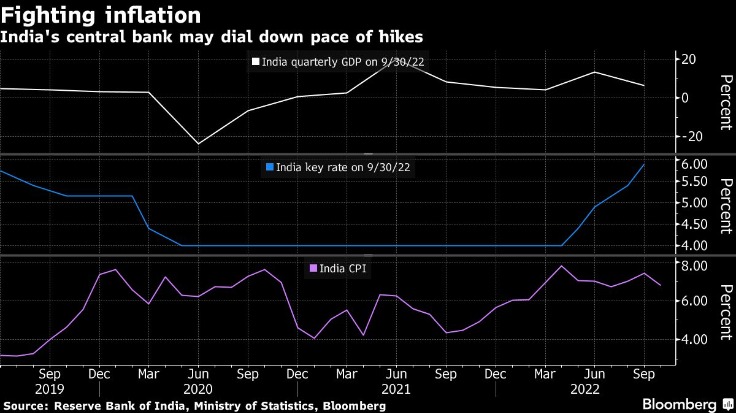
In its last scheduled meeting of the calendar year, the Monetary Policy Committee of the Reserve Bank of India voted to raise the benchmark policy repo rate by 35 basis points. It now stands at 6.25 per cent. The decision, in line with the consensus, was passed with a vote of 5-1 with member, Jayanth Varma, voting against the hike. The committee also kept its stance unchanged, pledging to remain focused on the withdrawal of accommodation. This stance was, however, objected to by two members, namely Jayanth Varma and Ashima Goyal. The growing dissent within the MPC suggests that, notwithstanding RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das’s statement that seems to indicate that the committee is not done raising rates, the rate hike cycle is nearing its peak.
Inflation, however, continues to remain a concern, despite its recent softening. In October, headline retail inflation fell to 6.77 per cent, from 7.41 per cent in September. However, much of the decline was on account of a fall in food inflation — the consumer food price index had declined to 7.01 per cent in October, from 8.6 per cent in September. But core inflation, which excludes the volatile food and fuel components, is not showing any signs of moderation. This suggests continuing price pressures in the economy. The RBI governor also noted in his statement that core inflation remains sticky. The policy statement is thus more hawkish than expected. It notes that the “battle against inflation is not over”, and further policy action is needed to keep “inflation expectations anchored, break core inflation persistence and contain second round effects”. Inflation has remained above the upper threshold of the RBI’s inflation targeting framework for 10 straight months. The central bank is, however, hopeful of price pressures easing in the economy. It has projected inflation at 6.6 per cent in the third quarter, trending thereafter to 5.9 per cent in the fourth quarter, and averaging 5.2 per cent in the first half of the next financial year.
Alongside, the RBI has also lowered its forecast for growth to 6.8 per cent this year, down from its earlier assessment of 7 per cent made in the September policy, and 7.2 per cent in the August policy. It noted that the changing assessments reflect the risks to growth from “protracted geopolitical tensions, tightening global financial conditions and slowing external demand.” Considering the changing economic conditions, the policy apparatus must be guided by the imperative of preserving macroeconomic stability.
-
Contain (verb) – restrain, curb, rein in, suppress, repress रोकना
-
Benchmark interest rate (noun) – It include repo rate, MSF rate, CRR rate, Bank rate etc.
-
Straight (adjective) – successive, in succession, consecutive, in a row, लगातार
-
Dissent (noun) – difference of opinion, argument, dispute, demur मतभेद, असहमति
-
Notwithstanding (adv/pre) – nevertheless, nonetheless, though के बावजूद
-
On account of (phrase) – because of, owing to, due to, as a consequence of, के कारण
-
Stance (noun) –attitude, stand, point of view, viewpoint, opinion, way of thinking
रुख
-
Moderation (noun) – reduction, diminishing, lessening, decrease, contraction कमी/नरमी
-
Repo rate (noun) – The interest rate that the RBI charges when commercial banks borrow money from it is called the repo rate.
-
Basis point (noun) – 100 basis point = 1%
-
Persistence (noun) – constancy, continuance, continuity, immortality, indestructibility, perpetuity
अटलता
-
Concurrence (noun) – Agreement, accord, consensus, harmony सहमति
-
Reflect (verb) – Indicate, show, display, manifest, exhibit, signify, suggest
दिखाना, प्रदर्शित करना
-
Forecast (noun) – prediction, prophecy, forewarning, prognostication
पूर्वानुमान
-
Protracted (adjective) – lengthy, prolonged, extended, long
लंबा
-
Fall (verb) – drop, collapse, sink, decline, slump
गिरना
-
Project (verb) – Predict, Predict, Envisage, Foresee
अनुमान लगाना
-
In line with (phrase) – in accordance with, according to, in keeping with
, के अनुसार
-
Price pressure (noun) – inflation caused by an increase in prices of inputs like labour, raw material, etc.
-
Preserve (verb) – keep, maintain, save, conserve
बनाए रखना
-
Hawkish policy (noun) – under this policy, policymaker is willing to allow interest rates to rise in order to keep inflation under control.
-
Inflation expectation (noun) – the rate at which people—consumers, businesses, investors—expect prices to rise in the future.
-
Alongside (adverb) – Together with, along with, in conjunction with
साथ - साथ
-
Hike (noun) – Increase
बढ़ोतरी
Apparatus (noun) – system, arrangement, regime, mechanism.
तंत्र
-
Anchor (verb) – secure, fasten, attach, connect firmly
से जोड़ना/ बांधना
-
Object (verb) – raise objections, express objections to, raise objections to, express disapproval,
आपत्ति उठाना, एतराज़ करना
-
Consider (verb) – Think, believe, deem, judge
विचार करना
-
Imperative (noun) – An essential or urgent thing.
अनिवार्यता
-
Assessment (noun) – Calculation, appraisal, estimation, consideration, measurement
मूल्यांकन
-
Softening (noun) – Reducing, diminishing, mitigating, allaying, lessening
कमी, घटौती
-
Core inflation (noun) – Core inflation is inflation-related to all the commodities, goods, and services in the economy minus the volatile food prices and fuel prices
-
Volatile (adjective) – Instable, unstable, changeable, capricious, fickle
अस्थिर
-
Sticky (adjective) – (used about a situation) difficult or unpleasant
(स्थिति) कठिन या अप्रिय
-
Monetary policy committee (MPC) (noun) – it is responsible for fixing the benchmark interest rate in India. The meetings of the Monetary Policy Committee are held at least four times a year and it publishes its decisions after each such meeting.
-
Concern (verb) – worry, trouble, disturb, upset, bother, disquiet
चिंतित करना
-
Peak (noun) – the point at which something is the highest, best, strongest, etc.
चरम पर
-
Pledge (verb) – Promise solemnly and formally; vow, plight, undertake
संकल्प/प्रतिज्ञा करना
-
Headline inflation (noun) – a measure of the total inflation within an economy, including commodities such as food and energy prices (e.g., oil and gas), which tend to be much more volatile and prone to inflationary spikes
-
Consumer Food price index (noun) – it is designed to measure the changes over time in general level of retail prices of selected goods and services that households purchase for the purpose of consumption.
-
Second round effect (noun) – These indirect effects of higher energy prices on the overall rate of inflation are called second-round effects
-
Upper threshold (noun) – The threshold inflation level for India is 6 per cent
-
Inflation targeting framework (noun) – a monetary policy where the central bank sets a specific inflation rate as its goal
-
Tightening (noun) – Tightening of monetary policy is implemented when the inflation is rising rapidly. When monetary policy is tightened, the interest rates are increased by the Central bank
-
Macroeconomic stability (noun) – Macroeconomic stability exists when key economic relationships are in balance—for example, between domestic demand and output, the balance of payments, fiscal revenues and expenditure, and savings and investment.